Kubernetes Plugin
The Kubernetes plugin for Backstage extends the core Backstage Developer Portal by integrating Kubernetes information directly into your entities. It provides a unified view of Kubernetes workloads across clusters, enabling service owners to monitor the health of their services without switching contexts.
With the Kubernetes plugin, you can:
-
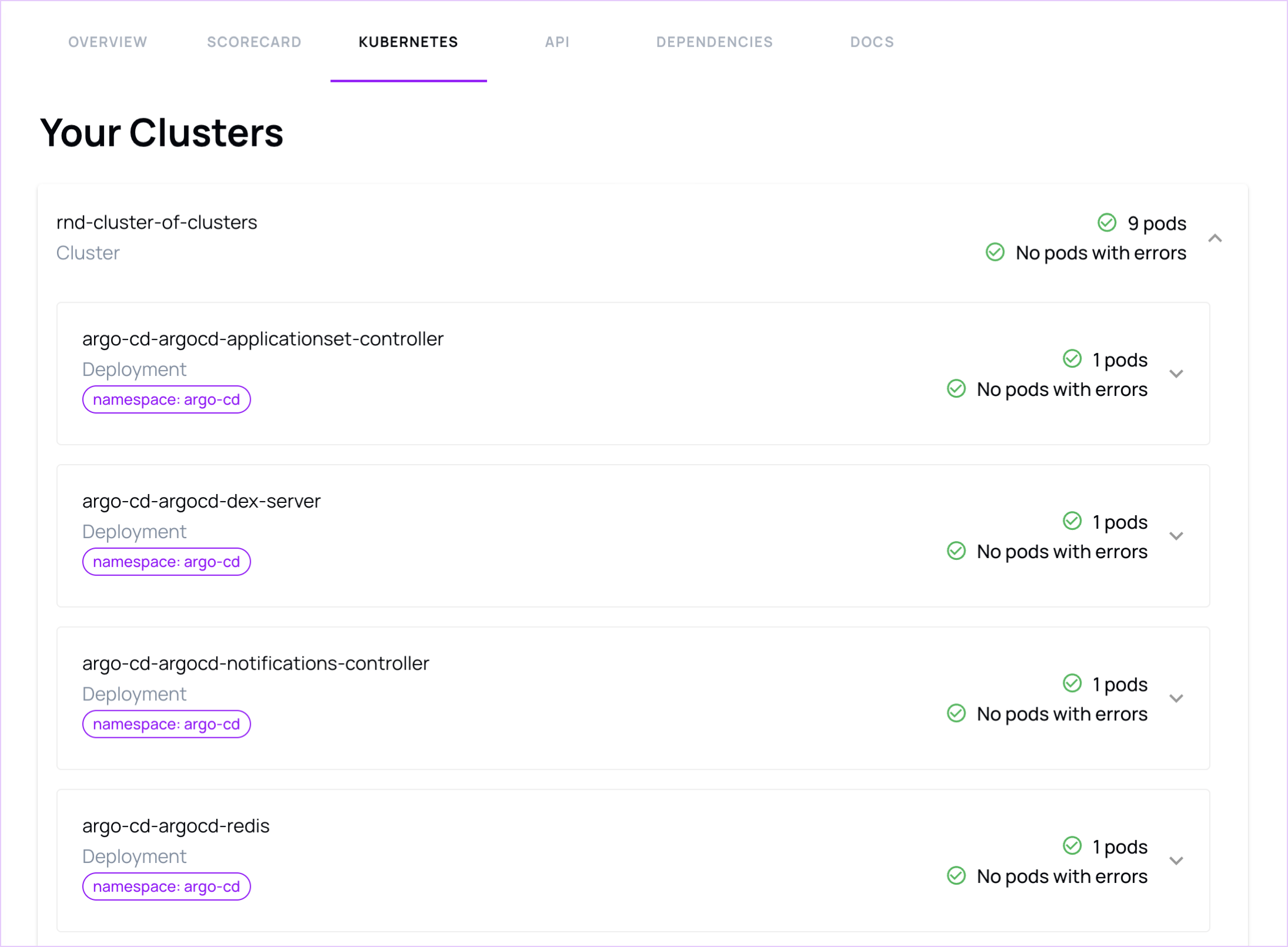
Visualise deployments across clusters: The plugin aggregates pods, deployments, and ReplicaSets from multiple clusters into a single view. This means you can see all your service's deployments in one place instead of switching kubectl contexts.
-
Receive automatic error reports: The plugin highlights errors in Kubernetes resources so you can see failing pods or deployments without running multiple commands.
-
Review autoscaling insights: The UI shows how close your service is to its autoscaling limit across clusters, helping you prepare for load spikes.
-
Cloud‑agnostic: Because the plugin calls the Kubernetes API directly, it works the same whether you deploy on AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, OpenShift or any other platform.
-
Improve your developer experience: By surfacing Kubernetes data inside the Venue Dashboard catalog, the plugin helps reduce the infrastructure complexity developers face. You can monitor deployments, view cluster health and troubleshoot issues without leaving Venue, unless you absolutely need to.
Required Configuration
To connect with the Kubernetes plugin, you need to define at least one cluster in the plugin settings. Each cluster must provide the following fields:
| Field | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster URL | ✅ | The base URL of the Kubernetes API server. You can obtain this by running kubectl cluster-info against the target cluster. The plugin uses this URL to query pods, services, and other resources. |
| Cluster Name | ✅ | A unique name for the cluster. This name is referenced in entity annotations when selecting clusters. |
| Service Account Token | ✅ | A bearer token is used to authenticate to the cluster. To retrieve it, create a ServiceAccount with read‑only privileges and extract its token. See the note below for additional details. |
| CA Data (Base64 encoded) | ✅ | The base64‑encoded certificate authority data for the cluster, which allows the plugin to verify the cluster’s TLS certificate.. You can copy the certificate-authority-data value from your ~/.kube/config file or run kubectl config view --raw --minify and extract the certificate-authority-data. |
| Dashboard URL | ❌ | (Optional) The URL of the Kubernetes Dashboard for your cluster. This must be a valid HTTP or HTTPS URL, which the plugin validates before saving. If provided, the plugin will be linked directly to the dashboard UI. |
The service account you provide must have at least read-only access to pods, services, configmaps, deployments, replicasets, horizontalpodautoscalers (HPA) and ingresses. Without these permissions, the plugin cannot display cluster resources.
Kubernetes v1.21+ transitioned from static, never-expiring service account tokens to short-lived "bound" tokens issued through the TokenRequest API. These bound tokens expire when the pod is deleted or after a set duration—defaulting to one hour—and the kubelet refreshes them automatically. The plugin reads the cluster from outside Kubernetes and cannot rely on the kubelet to refresh a bound token, so an hourly expiry would force you to manually rotate the token every hour.
Kubernetes still supports issuing a long‑lived token by creating a Secret of type kubernetes.io/service-account-token. For more information on how to do this, see the Kubernetes documentation.
Entity Configuration
Once a cluster is configured, tell the plugin which Kubernetes resources belong to a particular service by adding one or more of the following annotations to your component:
| Reference | Description |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes ID | A unique identifier that links an entity to Kubernetes resources. Add this annotation to the entity and add the same label (kubernetes-id) on your Kubernetes resources. |
| Kubernetes label selector | A comma-separated list of key=value pairs used to select resources, e.g., app=my-app,component=front-end. The plugin uses this selector to find objects in the cluster. |
| Kubernetes cluster name | When using the singleTenant service locator, specify the name of the cluster (matching the cluster name in the plugin configuration) to limit resource lookup to that cluster. |
| Kubernetes namespace | (Optional) Overrides the namespace used when retrieving resources. This can be helpful if your service runs in a specific namespace. |
The Venue.sh plugin enforces that a cluster name is specified and at least one of kubernetes-id or kubernetes-label-selector must be present. If you omit the namespace annotation, the plugin defaults to searching all namespaces.
Once this has been configured, the Kubernetes tab will become visible on your entity.